The Three Basic Principles of Statistical Design of Experiments Are
Principles of experiment design. These principles make a valid test of significance possible.

Design Of Experiments An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
An experiment is double blind if both the subjects and the researchers measuring responses are.
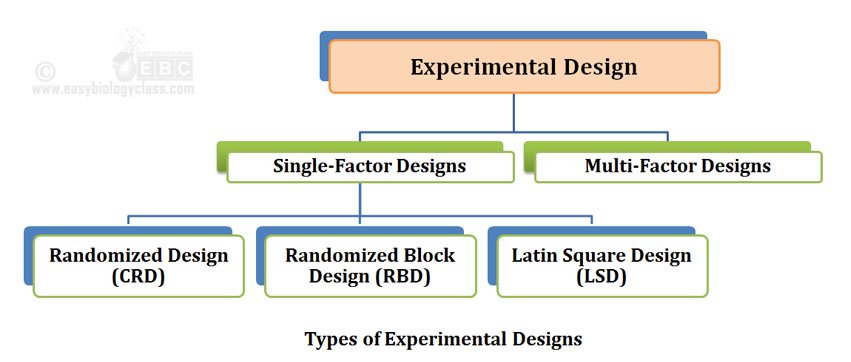
. Professor Fisher has enumerated three principles of experimental designs. Experimental design Basic principles 1. The basic principles of experimental design are i Randomization ii Replication and iii Local Control.
The basic principles of experimental designs are randomization replication and local control. Introduction to Design of Experiments. Ø The increased efficiency and reduced experimental errors in experimental designs are achieved by THREE.
Experimental variable with control variable 1 or EV CV 1. Introduction to Design of Experiments. The three basic principles of statistical design of experiments are A control comparison confounding.
In this article we will discuss about- 1. Control the effects of lurking variables on the response by ensuring all subjects are affected similarly by these lurking variables. Randomize to avoid confounding between.
B control randomization repetition. Basic Principles Z X Y We must control Z or include it. Stratification aka blocking 6.
Control variable 1 with control variable 2 or CV1 CV2. The three basic principles of statistical design of experiments are Control Randomization and Repetition. An experiment is blinded if the subjects do not know which treatment group they are in.
Meaning of Experimental Designs. 11 - A Quick History of the Design of Experiments DOE 12 - The Basic Principles of DOE. Increase the efficiency of design B.
C blocking blinding bias avoidance. One-shot Case Study Experimental Research Design. They hire a group of physical.
11 - A Quick History of the Design of Experiments DOE 12 - The Basic Principles of DOE. Control Experimental Blocking Matching. 113 The Four Principles of Experimental Design 1.
Then simply compare two or more treatments. 13 - Steps for Planning Conducting and. Control the effects of lurking variables on the response most simply by comparing two or more treatments.
Each of them is described briefly in. There are three basic principles behind any experimental design. Reduce the experimental errors.
Formulate questiongoal in advance 2. One-group Pretest-posttest Experimental Research Design. The principle of replication.
Thus each treatment is applied. Principles of Experimental Designs 3. A footwear company wants to test the effectiveness of its new insoles designed to prevent shin splints resulting from running.
In a experiment we must control hold constant other possible causes of X. The basic principles of statistical design of experiments are. Meaning of Experimental Designs 2.
Randomization is the cornerstone underlying the use of. When we say the design of an experiment or experimental. The random allocation of treatments to the experimental units.
The experiment should be reaped more than once. Experimental variable with control variable 2 or EV CV 2. 13 - Steps for Planning Conducting and.
Design of experiment provides a method by which the treatments are placed at random on the experimental units in such a way that the responses are estimated with the utmost precision. Components of an Experiment Terminology Experimental Design I Terminology Experimental Design II Main Principles of experimental design. This is the most accurate form of.
Control sources of variation other than the factors being tested by making conditions as similar as possible for all treatment.

Colour Wheels Colour Systems Color Wheel Color Themes Color Theory
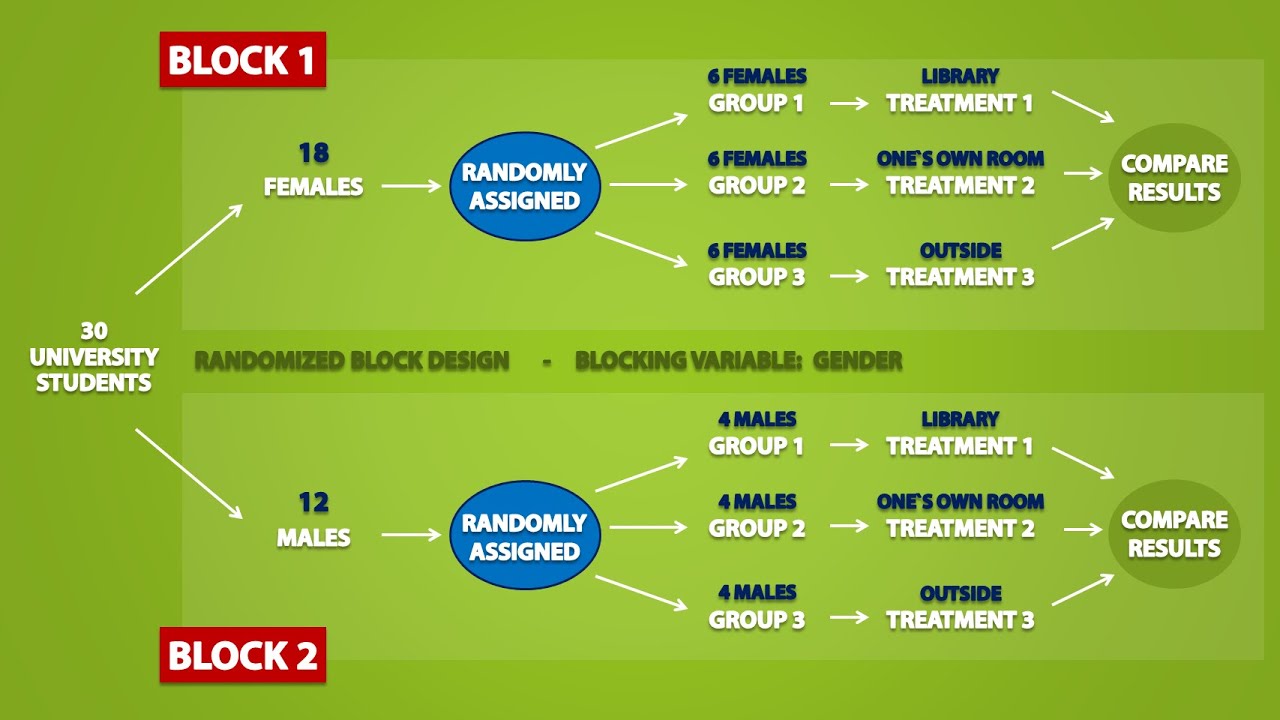
Types Of Experimental Designs 3 3 Youtube

Color Theory The Color Wheel Color Wheel Color Theory Color Harmony
Comments
Post a Comment